Shrinking Lakes - A Serious Concern
Water is vital to human survival. Thus the many shrinking lakes around the world are quite alarming.
The evaporation of lakes, along with other climate change aspects like lake levels, precipitation, and ice cover, are monitored closely.
Studies have confirmed that the evaporation of lakes has increased in recent years.
Lakes are shrinking due to climate change and human activity around the world, including Bolivia, the Middle East, China, and West Africa (Source).
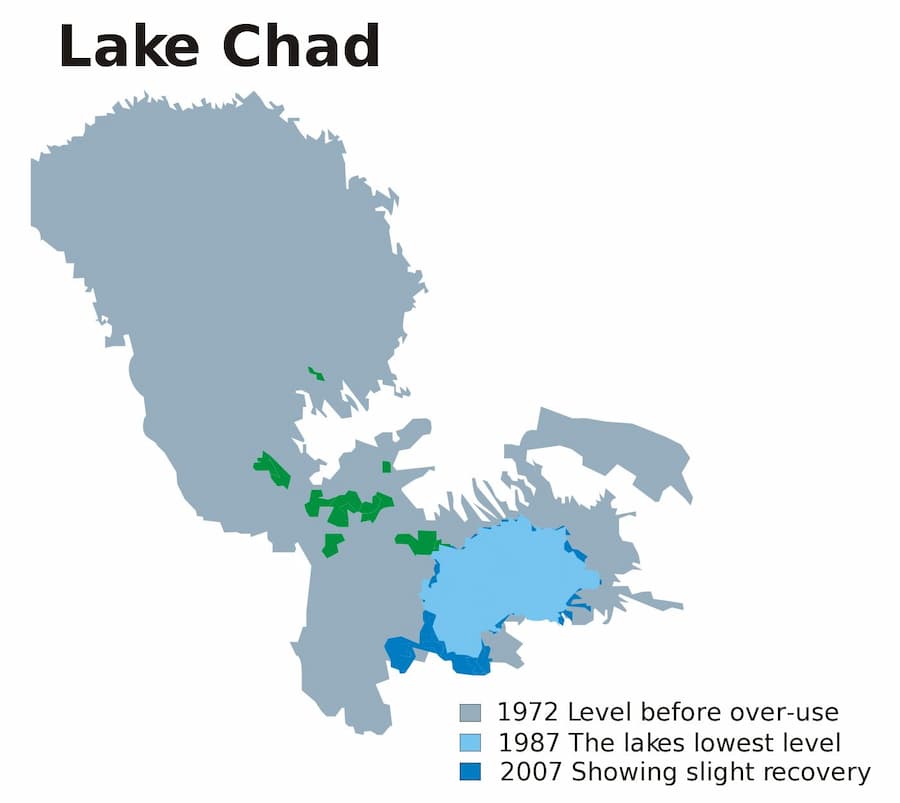
Lake Chad
The shrinking of Lake Chad in Africa is a quintessential example.
This reduction in size is due to climate change, as well as an increase in population and unplanned irrigation (Source).
The lake is large and shallow, but through decades its size has changed considerably.
The UN Environment Programme reports that the lake shrank by 95% from around 1963 to 1998 (Source).
Like other large lakes, Lake Chad is of great economic importance. In fact, it provides water to more than 30 million people in four different countries: Chad, Cameroon, Niger, and Nigeria (Source).
Unfortunately, 10.7 million people in the Lake Chad region require humanitarian relief to survive, according to the UN. In fact, due to desertification, it has become increasingly hard for families to make a living via agriculture, fishing, and livestock farming (Source).
Temperatures in the region of Lake Chad have risen one and a half times faster compared to the global average. Fortunately, the lake's size has been stable (or may even be growing) in recent years, and there is a plan to restore Lake Chad, but it may cost as much as 50 billion dollars (Source).
Therefore, public education about climate change and its impact on shrinking lakes are of great importance.
Rate of Evaporation and Effects on Infrastructure
When the temperature is high, the evaporation of lakes also increases, as well as the precipitation.
Researchers claim that if the rate of evaporation continues to increase, the infrastructures surrounding the lakes, including the canals and ports, will be affected.
Why? Because the primary basis for the infrastructure design is a consistent water level.
Hence, if there is too much evaporation, the water level will be reduced as well.
NASA Study on Warming Lakes
According to a research study of 235 lakes across six continents, lakes are warming by 0.34 degrees Celsius (0.61 Fahrenheit) each decade. These findings are based on more than 25 years of ground measurements and satellite temperature data. This rate is faster than the rate at which the oceans and the atmosphere are warming up (Source).
Rapid temperature increases may endanger life forms in a lake and may even cause them to disappear altogether (Source).
Surface water is important not just for drinking water but also for manufacturing, energy production, and the irrigation of crops. Also, protein from freshwater fish serves as vital nutrition for people in developing countries (Source).
Also, as lakes continue to warm, there will be increased instances of algal bloom, including those that are toxic to fish and animals. There will be an increase in the emissions of methane by 4% over the next decade if trends continue (Source).
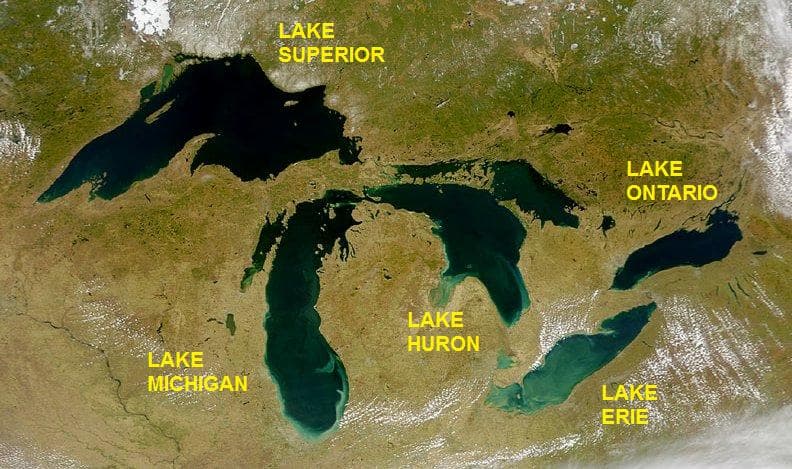
The Great Lakes - 2014 Research
In 2014, researchers claimed that evaporation is higher than precipitation, and it will only have one result – lower levels of water (Source).
From 1998 to 2014, the water levels of the great lakes have declined. Carl Watras, a climate scientist, stated: "The last two decades have been kind of exceptional." He also added, "Our lakes have never been lower than they are" (Source).
The resulting changes in the water levels are due to climate change.
According to research from 2014, if this problem is not addressed, the Great Lakes that people love will continue to decrease in size.
This shrinking could cause billions of dollars in losses by industry and tourism (Source).
According to Peter McIntyre, a professor from the University of Wisconsin-Madison Center for Limnology, "Changes in water temperatures are really a major threat in the Great Lakes. It's a pretty acute shift" (Source).
In general, scientists at that time stated that their water levels are highly sensitive to climate change and will continue to decline.
Seesawing Water Levels of Great Lakes - 2019 Reports
However, according to new research from 2019, climate change is causing extremes in water levels in the Great Lakes. On the one hand, there is more evaporation, which causes lower levels, and on the other hand, there is more precipitation due to increased atmospheric moisture, which causes higher levels (Source).
Essentially, when weather patterns are dry, they are very dry, and when they are wet, they are very wet (Source).
Blair Feltmate, a professor and head of Waterloo's Intact Centre on Climate Adaptation stated: "We’re getting more water coming down over shorter periods of time more frequently" (Source).
Feltmate adds, "Now, when the big storms hit, the water goes very quickly into the Great Lakes" (Source).
In 2019, water levels for the great lakes were at record highs which can lead to faster erosion of the coastline as well as more flooding (Source).
"It's uncertain how climate change will affect water levels in the Great Lakes, which already fluctuate periodically, the scientists said" (Source).
"While annual U.S. precipitation increased four per cent between 1901 and 2015, it jumped nearly 10 per cent in the Great Lakes region. Much of that increase was due to unusually large storms, the report says" (Source).
"Warmer temperatures will produce less ice cover, boosting evaporation and pushing levels down. However, they could rise in years with especially heavy precipitation and temporary deep freezes caused by southward migration of frigid polar air" (Source).
Therefore, climate change will definitely impact the great lakes by bringing in more extreme weather, but it's not clear exactly how it will affect water levels in the long run.
Preserving Our Water to Combat Shrinking Lakes
The evaporation of lakes must be prevented because it can have ecological and economic consequences.
Shrinking lakes will further aggravate the concurrent problem of shortages of food and water around the globe.
To combat this phenomenon, climate change must be addressed, along with other factors like ice cover and precipitation.
Everyone must help in addressing climate change, preserving the lakes, and making this world a better place.

From National Geographic
Further Reading and Sources
- Wikipedia
- BBC News
- CBC News
- CTV News
- NASA
- The Guardian Article on Lake Chad
- The Guardian Article on Great Lakes
- The Guardian Article on Shrinking Lakes Around the World
- Scientific American Article from 2014
- Scientific American Article from 2019
Join the Community and Newsletter (4500 Subscribers)
You can subscribe to my Substack Page or see the archives of previous posts. More great content coming soon!
Recent Articles
-
Quotes on Climate Change
Nov 24, 25 07:29 PM
Here is a list of quotes on climate change divided into different categories, many of which include people you have previously heard of. -
Climate Change Guide
May 09, 25 08:36 PM
The Climate Change Guide is your guide to a more sustainable future, and will provide you with all relevant information on mankind's greatest challenge. -
Laurent Cousineau
May 09, 25 08:23 PM
Here is information about the founder of the website Climate Change Guide, Laurent Cousineau. He created it in August 2011. -
Climate Change Quotes by Scientists Around the World
Aug 24, 24 02:01 PM
Explore impactful climate change quotes by scientists. Discover the wisdom and insights of experts advocating for a sustainable future.