The Ozone Layer Crisis: A Global Phenomenon
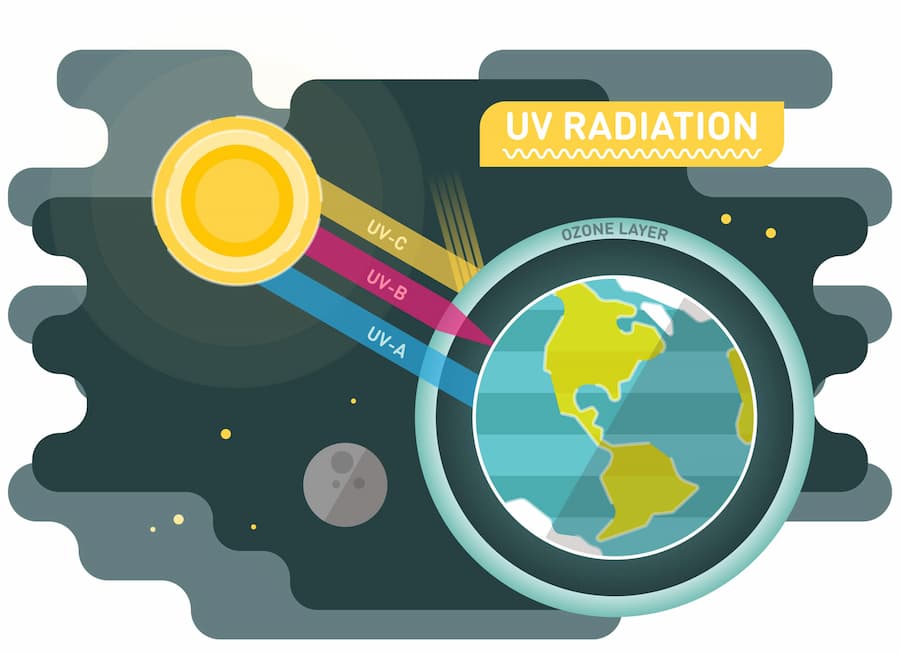
The ozone layer protects us from the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation, notably skin cancer and cataracts.
A lot of people get confused between climate change and this particular topic so I hope this article will clear things up.
In the year 1985, a groundbreaking scientific revelation emerged from the icy expanse of Antarctica—an alarming hole in Earth's ozone layer. The ozone layer acts as a crucial protective shield, safeguarding us from the sun's harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays.
This unexpected phenomenon stirred scientists worldwide, revealing the detrimental consequences of human activities on our planet's delicate atmospheric balance. The discovery shed light on the role of ozone-depleting chemicals, which had permeated everyday items such as air conditioners and aerosol cans, leading to far-reaching environmental implications.
The Ozone Layer's Vulnerability
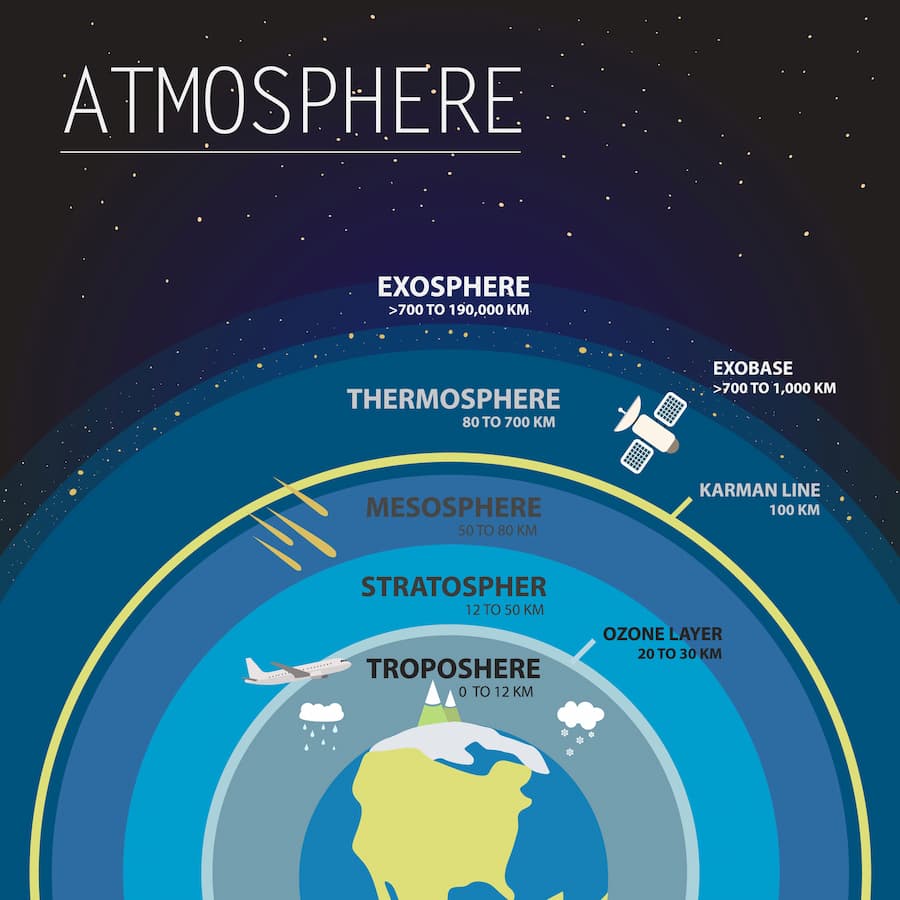
The ozone layer, situated in the Earth's stratosphere, acts as a natural filter, absorbing the majority of the sun's harmful UV radiation. In the early 1980s, scientists first began to notice a decline in ozone levels above Antarctica. Eventually, they identified a significant depletion, popularly known as the "ozone hole." It became clear that the culprits were certain industrial chemicals known as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs), and halons. These compounds were extensively used in the production of refrigerants, solvents, and aerosol propellants due to their stability and non-flammability.
The Impact of Ozone-Depleting Chemicals
The stable nature of these chemicals allowed them to persist in the atmosphere, eventually reaching the stratosphere. There, the sun's intense UV rays acted as a catalyst, breaking down these compounds and releasing chlorine and other ozone-destroying substances. The harmful consequences were manifold. Increased UV radiation reaching the Earth's surface posed risks to human health, causing skin cancer, cataracts, and suppressed immune systems. Moreover, the altered UV levels disrupted ecosystems, affecting aquatic life, plant growth, and even the stability of food chains.
International Response and the Montreal Protocol
Recognizing the urgent need to address this impending environmental crisis, the international community swiftly mobilized. In 1987, more than 200 countries signed a landmark treaty known as the Montreal Protocol. This historic agreement sought to eliminate the production and use of ozone-depleting substances. The collaboration and dedication exhibited by nations across the globe demonstrated the capacity for collective action when faced with a common threat.
The Ozone Layer's Recovery and Unintended Benefits
Thanks to the Montreal Protocol, the world witnessed a significant shift in the use of ozone-depleting chemicals. As countries phased out their production and implemented alternatives, the ozone layer embarked on a path to recovery. The reduction in the release of these chemicals had an unexpected positive consequence—it also curtailed the emission of greenhouse gases. Many of the substances damaging the ozone layer were also potent contributors to global warming. By limiting their use, humanity unintentionally mitigated the rate of climate change and its subsequent impacts.
Preservation of Arctic Sea Ice
The preservation of Arctic sea ice emerged as an additional and invaluable consequence of banning ozone-depleting chemicals. These substances, in addition to their role in ozone depletion, possessed properties that enhanced their greenhouse effect potential. As the Montreal Protocol successfully curbed their usage, it inadvertently prevented the release of significant greenhouse gases. Consequently, more than half a million square kilometers of Arctic sea ice were spared from melting, preserving vital ecosystems and ensuring the region's ecological balance.
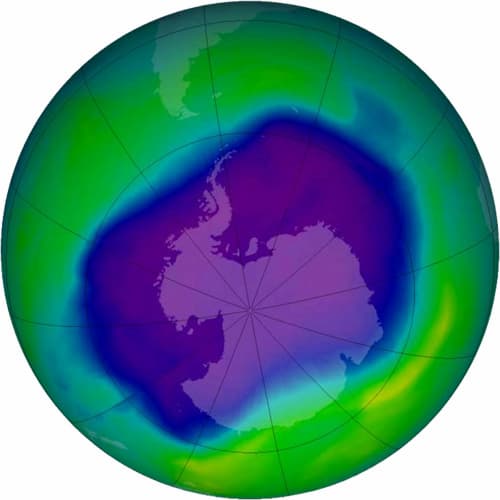
The largest Antarctic ozone hole ever recorded was in 2006. The blue and purple colors denote where there is less ozone, whereas the greens, yellows, and reds represent where there is more ozone.
The Arctic's Fragile Future
Despite the remarkable progress made in the recovery of the ozone layer and its cascading benefits, the Arctic remains under threat due to climate change. The fate of this vulnerable region hinges upon collective action to limit global warming. If humanity fails to alter its current trajectory, scientists project the first "ice free" summer in the Arctic to occur around the middle of this century. This disheartening projection serves as a stark reminder that the efforts undertaken through the Montreal Protocol have only delayed the inevitable by approximately 15 years. The Arctic, with its unique ecosystems and significance in regulating global climate patterns, stands at a critical crossroads.
The rapid changes witnessed in the Arctic highlight the urgency of addressing climate change on a global scale. Rising temperatures have already caused a reduction in the extent and thickness of sea ice, disrupting the delicate balance that sustains numerous species, including polar bears, seals, and marine birds. Moreover, the melting of Arctic ice contributes to the rise in sea levels, exacerbating the risks faced by coastal communities around the world.
To safeguard the Arctic and mitigate the detrimental effects of climate change, concerted and immediate action is necessary. The lessons learned from the successful phase-out of ozone-depleting chemicals can serve as an inspiration and blueprint for addressing the broader challenges of climate change. The international community must come together once again, transcending borders and political differences, to implement comprehensive strategies that reduce greenhouse gas emissions, promote renewable energy sources, and foster sustainable practices across sectors.
Raise Awareness About the Ozone Layer Issue
Furthermore, public awareness and engagement are crucial elements in driving meaningful change. Educating individuals about the interconnectedness of the ozone hole issue, climate change, and the Arctic's fate can inspire them to adopt environmentally conscious behaviors and advocate for stronger environmental policies. Governments, educational institutions, and organizations must collaborate to enhance environmental literacy, empowering individuals to become stewards of the planet.
In parallel, research and innovation play a pivotal role in developing cutting-edge technologies and solutions. Continued scientific exploration of the Arctic region can provide invaluable insights into the complex dynamics of climate change and its cascading effects. By expanding our understanding of the Arctic ecosystem, we can enhance adaptation strategies, develop sustainable resource management practices, and strengthen the resilience of both the region and its inhabitants.
Need for Collective Action
Furthermore, public awareness and engagement are crucial elements in driving meaningful change. Educating individuals about the interconnectedness of the ozone hole issue, climate change, and the Arctic's fate can inspire them to adopt environmentally conscious behaviors and advocate for stronger environmental policies. Governments, educational institutions, and organizations must collaborate to enhance environmental literacy, empowering individuals to become stewards of the planet.
In parallel, research and innovation play a pivotal role in developing cutting-edge technologies and solutions. Continued scientific exploration of the Arctic region can provide invaluable insights into the complex dynamics of climate change and its cascading effects. By expanding our understanding of the Arctic ecosystem, we can enhance adaptation strategies, develop sustainable resource management practices, and strengthen the resilience of both the region and its inhabitants.
The following video gives a good summary of this issue:

ChatGPT was used to help create this article
Further Reading and Sources
Join the Community and Newsletter (4500 Subscribers)
You can subscribe to my Substack Page or see the archives of previous posts. More great content coming soon!
Recent Articles
-
Quotes on Climate Change
Nov 24, 25 07:29 PM
Here is a list of quotes on climate change divided into different categories, many of which include people you have previously heard of. -
Climate Change Guide
May 09, 25 08:36 PM
The Climate Change Guide is your guide to a more sustainable future, and will provide you with all relevant information on mankind's greatest challenge. -
Laurent Cousineau
May 09, 25 08:23 PM
Here is information about the founder of the website Climate Change Guide, Laurent Cousineau. He created it in August 2011. -
Climate Change Quotes by Scientists Around the World
Aug 24, 24 02:01 PM
Explore impactful climate change quotes by scientists. Discover the wisdom and insights of experts advocating for a sustainable future.